报名编号:CICC2969
团队名称:火锅队
学校名称:广东工业大学
参考帖[求助]使用NMSIS-NN库时,出现section `.bss' will not fit in region `ram'错误怎么结局可以知道,编译 NMSIS 的官方例程需要修改软件代码中的 ilm 和 ram 的地址长度。软件修改后,在硬件方面也必须要配合着修改,否则装不下那么多程序。根据笔者的实验,若不修改硬件的数据存储容量,板子在 2 分钟内没办法输出结果。
原E203的 ITCM 和 DTCM 的大小在文件“config.v”中做了规定:它们的地址位宽都为16位,起始地址分别为 0x8000_0000 和 0x9000_0000。如下图:
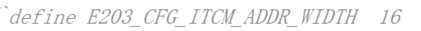
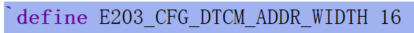
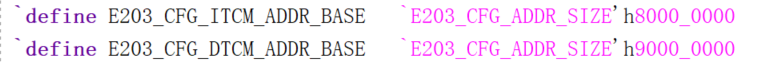
为了扩大E203的ITCM 和 DTCM ,就要修改 ITCM 和 DTCM 的地址位宽。笔者将他们都修改为 18 位。此时 BRAM 使用量从 32 变成了 128个,但 NMSIS 的例程就能在几秒内输出结果。需要注意的是,修改了 ITCM 和 DTCM 的地址位宽后, vivado 会提示太多扇入扇出而无法 Implementation,Log中会提示 “HACOOException,no stack trace available, please use hs_err_<pid>.dmp ins”。此时只需要在 Tcl Console 中输入 "get_param pwropt.maxFaninFanoutToNetRatio 2000"就行了。
以上就是本帖关于修改 E203 的 ITCM 和 DTCM 的内容!
最后,笔者希望有更多的关于优化 BRAM 的帖子被分享出来,已解决扩大 ITCM 和 DTCM 后 BRAM 使用量猛增的问题。
